|


_____________
In this section of
Gaspee History


____________
Go the section on
Gaspee Raiders
for biographical
information on the Americans in the boats attacking the Royal Navy ship
Gaspee.
_____________
Books: American Colonial and
Revolutionary War history or the people involved. We have suggestions
for you.

_____________
Copyrighted.
© 2005
to Oct.2009, Leonard H. Bucklin.
-----
The
content of this site may not be reproduced except for brief excerpts for
reviews or scholarly references..
See
Copyright Notices,
Privacy Policy, and Warnings & Disclaimers.
_____________

This is a history education and
research web site of the
Joseph Bucklin Society.
 References
in brackets [ ] or in curly brackets { } on any page in
this website are to books, or other materials, listed in the Joseph
Bucklin Society Gaspee Bibliography, or to materials held by the Joseph
Bucklin Society. References
in brackets [ ] or in curly brackets { } on any page in
this website are to books, or other materials, listed in the Joseph
Bucklin Society Gaspee Bibliography, or to materials held by the Joseph
Bucklin Society.
|
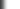
|
Brigentines Described
 General description of a colonial ship type
named a "brigantine", often used as a privateer. General description of a colonial ship type
named a "brigantine", often used as a privateer.
Brigantine. The brigantine was the second most popular type of ship built in the American
colonies before 1775. (The most popular ship type was a
"sloop.")
A brigantine is a vessel swifter and more easily maneuvered
than a sloop or schooner, and hence employed for purposes of piracy, espionage, and
reconnoitering, and as an outlying attendant upon larger ships for protecting
the larger ship, or for
supply or landing purposes in a fleet of ships.
The brigantine was generally larger than a sloop or schooner. However,
the brigantine was a vessel that could be of various sizes, ranging from 30 to 150 tons burden.
 Generally, in the 1700's a brigantine was a two masted sailing ship, having on the main mast both (1) a fore-and-aft main sail ( a triangular type of
sail) and also (2) a square main topsail. The fore-and-aft main sail
has an advantage over a square sail of being able to be better maneuvered and to
allow better sailing of the ship.) But after 1720 the main
[square] topsail was omitted in most brigantines in favor of a large main sail. Generally, in the 1700's a brigantine was a two masted sailing ship, having on the main mast both (1) a fore-and-aft main sail ( a triangular type of
sail) and also (2) a square main topsail. The fore-and-aft main sail
has an advantage over a square sail of being able to be better maneuvered and to
allow better sailing of the ship.) But after 1720 the main
[square] topsail was omitted in most brigantines in favor of a large main sail.
The 1780 Universal Dictionary of the Marine by William Falconer further
defined a brigantine as:
Brigantine . . . Among English seamen, this vessel is
distinguished by having her [fore-and-aft] main-sail set nearly in the plane of
her keel; whereas the main-sails of larger ships are hung athwart, or at right
angles with the ship’s length, and fastened to a yard which hangs parallel to
the deck: but in a brig, the foremost edge of the main-sail is fastened in
different places to hoops which encircle the main-mast, and slide up and down it
as the sail is hoisted or lowered: it is extended by a gaff above, and by a boom
below.
Converting a merchant brigantine into a privateer.
It did not take much to convert a brigantine from use as a merchant ship to
use as a privateer, or vice versa. That was because privateers avoided navy battles
with navy ships, first of all because the navy ship could be expected to
fight (whereas merchant ships frequently surrendered). Second, the
best prize of a privateer was a merchant ship loaded with goods that could be sold. Hence,
if merchant ships were the only ships likely to be attacked by a privateer,
a privateer merely needed small cannons, such as swivel guns, and relatively
small spaces for the storage of powder and ammunition.
A swivel gun was mounted in an iron fork that was shaped somewhat like an
oarlock. The iron fork was bolted to the outside of the
hull. One very popular type of swivel gun was about three feet long
and had a bore of about an inch and a half, with a wooden handle, about the
shape of baseball bat, attached to its breech. This handle was used from
the deck to aim the cannon.
Other popular types of swivel guns were the blunderbuss, which fired loose
shot, like a shotgun; and the howitzer, a shortened cannon with a larger bore.
Swivel guns were primarily used as anti-personnel weapons, rather than
as ship-sinking weapons. First of all, the object was to seize ships
and their cargo, not to sink them (which produced no profit). Second, the
shots a swivel gun could fire would produce relatively little damage to a
stout ship hull. Third the main ships of the navy's of the day had cannon with much longer
ranges than swivel guns, so the chances of ship with only swivel guns getting
close enough to a navel ship to sink it was small.
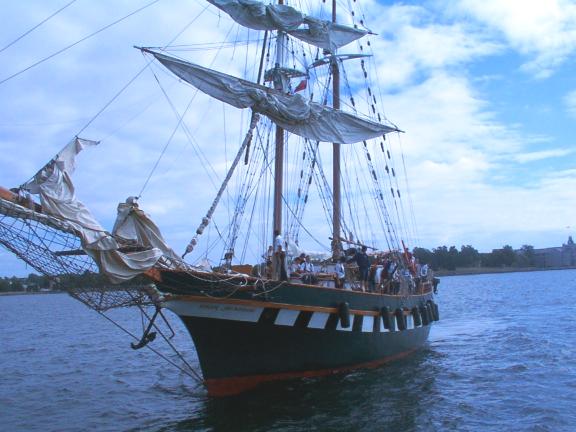
Here's a view of one of today's recreations of an 18th century brigantine.

|





